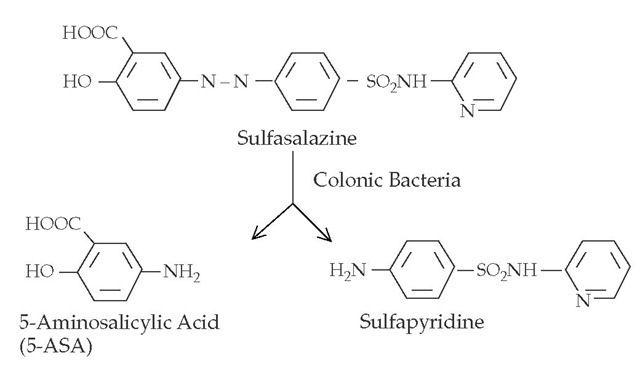
Sulfasalazine and 5-aminosalicylates in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
Sulfasalazine is metabolized in the body to 2 major components: Sulfapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). While 5-ASA is believed to be the main immunomodulator in Ulcerative Colitis, acting locally in the colon, Sulfapyridine is thought to be the active moiety in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Women With Autoimmune Diseases: Medications During Pregnancy and Lactation
Sulfasalazine is a useful DMARD especially for women planning pregnancy. Special cautions to bear in mind:
1) Increase folic acid supplement dose in pregnancy;
2) Avoid in early lactation.
Sulfasalazine and MTX in RA

Sulfasalazine and Methotrexate are not infrequently combined in the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, especially in the famed “triple therapy” regimen that is recently shown to be more cost-effective and sustainable than MTX in combination with a biologic anti-TNF. Yet, it is often mentioned that it is mechanistically illogical to combine SSZ with MTX, since they act in similar fashion.
Yes and No. They both interfere with folate metabolism (and DNA synthesis, in turn), but they individually have many other differing actions, some of which have not been thoroughly elucidated. MTX, for example, is recently reported to modulate JAK-STAT intracellular signaling. SSZ, on the other hand, is known to interact with the microbiome. While mechanistically they may even conflict with each other’s metabolism in vitro, there is clinical evidence that combination therapy is synergistic.